The role of histamine in allergy is well-known. What may be less well-known or considered is that histamine can negatively impact immunity.1 During the histamine response process, inflammatory cytokines, including IL3, IL4, IL5, IL8, IL13, TNF-alpha, and prostaglandin E2, are produced and circulate through the system, causing inflammation, allergic symptoms, and in some cases, histamine intolerance.2 The deleterious effects of this process, when overactive, may be chronic unresolved inflammation and compromised immunity.1 2
Does an Overactive Histamine Response Increase Susceptibility to Infection?
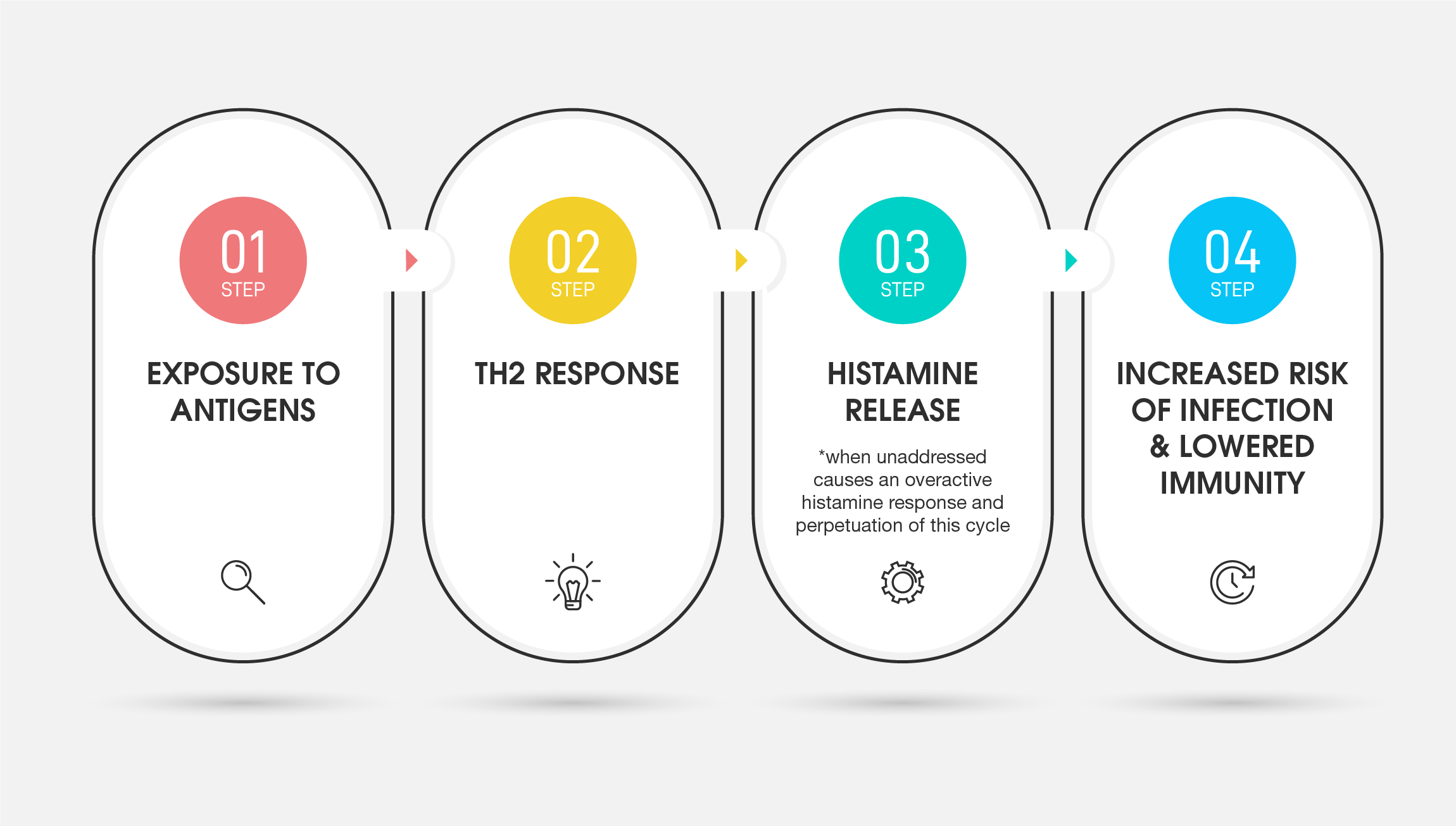
Under continuous exposure to antigenic environmental factors, the immune system is likely to become imbalanced. When this occurs, the body can become more susceptible to infection and autoimmunity.3 4 5 Some of this can be explained through the Th1/Th2 immune responses:
Th1 vs. Th2 Responses
Within the adaptive immune system, there are two main mechanisms of immunity taking place: cell-mediated immunity (does not involve antibodies) and humoral immunity (involves antibodies). Th1 cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity to fight against viruses, parasites, and intracellular infections via activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines. When Th1 cells are suppressed, an increased risk of intracellular injury and viral infection exists.1 6
Th2 cells are involved in humoral immunity, which is mediated by antibody molecules that are secreted by plasma cells. These helper cells mediate antibodies extracellularly to protect against infection.1 Some individuals have a Th2-dominant immune response, as commonly seen in autoimmune patients. Because of Th2 dominance, individuals often experience exacerbation of existing allergies, development of new allergies, and a compromised immune response. Th2 dominance is even thought to be the underlying cause of many autoimmune diseases.1
The Th2 response drives histamine release, and when this becomes overactive or goes unresolved, the cycle perpetuates itself. Thus, an overactive histamine response results in a weakened Th1 response, a more active Th2 response, and an increased risk of viral and bacterial infection.1 4
Histamine and System-specific Immunity
The Respiratory System
Histamine is a common trigger for acute immune-mediated reactions in the lungs through:
- Production of inflammatory cytokines
- Smooth muscle contraction in the lungs, known as bronchoconstriction
- Production of mucus in the respiratory tract
Specifically, the histamine response causes inflammation in the lungs through enhancing secretion of Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13), and inhibiting the production of Th1 cytokines (IL-2, interferon-gamma, and IL-12). As the histamine response causes inflammation and mucus accumulation in the respiratory tract, susceptibility of lung tissues to viral and bacterial infection increases.4 7 Thus, proper histamine control may help to lower risk of respiratory infection.
The Gastrointestinal System
The gastrointestinal (GI) system is home to roughly 70% of the body’s immune potential, namely through gut-associated and mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue.8 The gut is site to many important immune-mediated mechanisms including:
- Response to pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi
- Tolerance of self-antigens
- Tolerance to commensal flora
- Sensitization and desensitization to foods
A continuous histamine response often causes GI symptoms, including smooth muscle contraction, known as hyperperistalsis, and prolonged irritable bowel symptoms.6 9 To effectively support the GI system, and therefore the immune system, proper histamine balance should be addressed.
How to Limit an Overactive Histamine Response
There are various contributing factors to the amount of circulating histamine levels in the body, including:
- High histamine foods and foods that encourage histamine production
- Certain medications
- Environmental antigens including dust, pollen, etc.
- Hormone imbalances
- Physical and emotional stress
- Nutrient deficiencies
To effectively reduce the levels of circulating histamine, each of the above areas should be investigated. In addition, targeted nutritional compounds can also help to mitigate inflammatory pathways initiated by the histamine response.*
Nutritional Compounds That May Help Reduce Effects of Histamine*
Quercetin, may modulate inflammation in the airway, inhibit histamine production, and limit viral replication in an innate immune response.* 10 11 Mangosteen and stinging nettle both inhibit binding of histamine to the H1 receptor.* 12 13 Butterbur may regulate muscle contraction within the airway and cardiovascular system.*14 Ginger supports proper blood circulation, aids in digestive processes, and inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and TNF-alpha) involved in immune reactions.* 15 In addition to its well-known anti-inflammatory benefits, curcumin inhibits histamine release from mast cells.* 16
Related Nutritional Support Formulas
- Packard KA, Khan MM. Effects of Histamine on Th1/Th2 Cytokine Balance. Int Immunipharmacol. 2003;3(7):909-20.
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, Sato MN. Role of histamine in modulating the immune response and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;27;2018:9524075.
- Percival SS, Milner JA. Opportunities for research in immunonutrition. J Nutr. 2005;135;2921S-23S.
- Wang JY. The sticky relationship between allergies and infections. Asia Pac Allergy. 2015;5(3):133‐35.
- Rottem M, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y. Allergic disease and autoimmune effectors pathways. Dev Immunol. 2002;9(3):161‐67.
- Yazdanbakhsh M, Kremsner PG, Van Ree R. Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science. 2002;296(5567):490‐94.
- Komi D, Mortaz E, Amani S, Tiotiu A, Folkerts G, Adcock IM. the role of mast cells in IgE-independent lung diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Feb 21.
- Vighi G, Marcucci F, Sensi L, Di Cara G, & Frati F. Allergy and the gastrointestinal system. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;153;3-6.
- Weiner HL. Oral tolerance, an active immunologic process mediated by multiple mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:935-37.
- Mlcek J, Jurikova T, Skrovankova S, Sochor J. Quercetin and its anti-allergic immune response. Molecules. 2016;21(5):623.
- Wu W, Li R, Li X, et al. Quercetin as an antiviral agent inhibits influenza A virus (IAV) entry. Viruses. 2015;8(1):6.
- Chin YW, Kinghorn AD. Structural characterization, biological effects, and synthetic studies on xanthones from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana), a popular botanical dietary supplement. Mini Rev Org Chem. 2008;5(4):355-64.
- Roschek B Jr, Fink RC, McMichael M, Alberte RS. Nettle extract (Urtica dioica) affects key receptors and enzymes associated with allergic rhinitis. Phytother Res. 2009;23(7):920-26.
- Shimoda H, Tanaka J, Yamada E, Morikawa T, Kasajima N, Yoshikawa M. Anti type I allergic property of Japanese butterbur extract and its mast cell degranulation inhibitory ingredients. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54(8):2915-20.
- Kim Y, Kim DM, Kim JY. Ginger extract suppresses inflammatory response and maintains barrier function in human colonic epithelial Caco-2 cells exposed to inflammatory mediators. J Food Sci. 2017;82(5):1264-70.
- Zhang N, Li H, Jia J, He M. Anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin on mast cell-mediated allergic responses in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse. Cell Immunol. 2015;298(1-2):88-95. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.09.010
FDA Disclaimer
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
The nutritional support discussed herein applies to seasonal environmental allergies and should not be used to treat, cure, or prevent acute or chronic food-protein related allergies, such as peanut allergy.